https://doi.org/10.1351/goldbook.10218
Extraction of analytes from the gas phase or solution by a single drop of extraction solvent.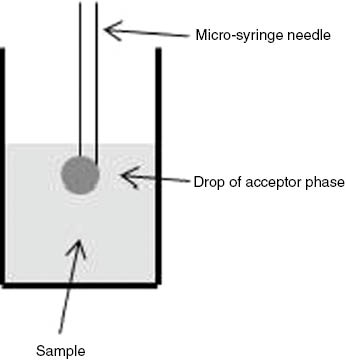
Notes:
- The extraction solvent with a volume typically \(\lt \pu{50 \upmu\!L}\) is suspended as a drop from the tip of a microsyringe needle as shown in the figure below.
- Typically, the sample is aqueous and the acceptor phase is an organic solvent, resulting in a two-phase extraction system (\(\ce{aqueous\!->\!organic}\)). SDME can also be operated in three-phase mode (\(\ce{aqueous\!->\!organic\!->\!aqueous}\)), or in the headspace mode (\(\ce{aqueous\!->\!gas\!->\!organic or aqueous}\)).
- The sample is stirred or agitated during extraction. After extraction, the drop of acceptor phase is collected by withdrawing it into the syringe used to support the drop for the final analytical measurement.

Typical experimental arrangement for single-drop microextraction.