https://doi.org/10.1351/goldbook.10209
Extraction in which a water-immiscible extraction solvent is continuously percolated through an aqueous solution and returned to the extraction solvent reservoir.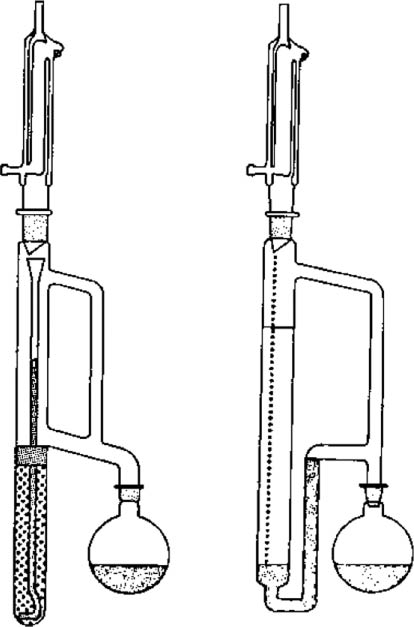
Notes:
- Typically, a fixed volume of extraction solvent is recycled through the aqueous sample solution by distillation and condensation, and dripped into the sample solution. A siphon mechanism allows continuous recovery of the extraction solvent based on its relative density.
- Typical apparatuses are shown below.
- Continuous liquid-liquid extraction techniques are used when the sample volume is large, the distribution constant is small, or the rate of extraction is slow.

Apparatus for continuous liquid–liquid extraction with a lighter-than-water extraction solvent (left) and a heavier-than-water extraction solvent (right). In each case the extraction solvent is contained in the round bottom flask and the aqueous sample in the vertical glass column.
Source:
PAC, 2016, 88, 517. 'Glossary of terms used in extraction (IUPAC Recommendations 2016)' on page 532 (https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2015-0903)
PAC, 2016, 88, 517. 'Glossary of terms used in extraction (IUPAC Recommendations 2016)' on page 532 (https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2015-0903)