https://doi.org/10.1351/goldbook.09603
Constitutional unit in a dendrimer molecule, from which the dendron(s) emanate(s).
Notes:
- The structure of the core unit may be identical to that of the constitutional repeating units.
- Occasionally, a dendrimer molecule may consist of two dendrons directly connected together.
- In a hyperbranched macromolecule obtained by the \({\rm{AB}}_{x}\mbox{-}\rm{type}\) monomer + \({\rm{B}}_{y}\mbox{-}\rm{type}\) monomer polycondensation approach, where \(\rm{A}\) and \(\rm{B}\) refer to mutually reactive groups, the terms core molecule (not acceptable) and core unit refer to the \({\rm{B}}_{y}\mbox{-}\rm{type}\) unit, even though the structure of the macromolecule does not comprise dendrons.
Example: 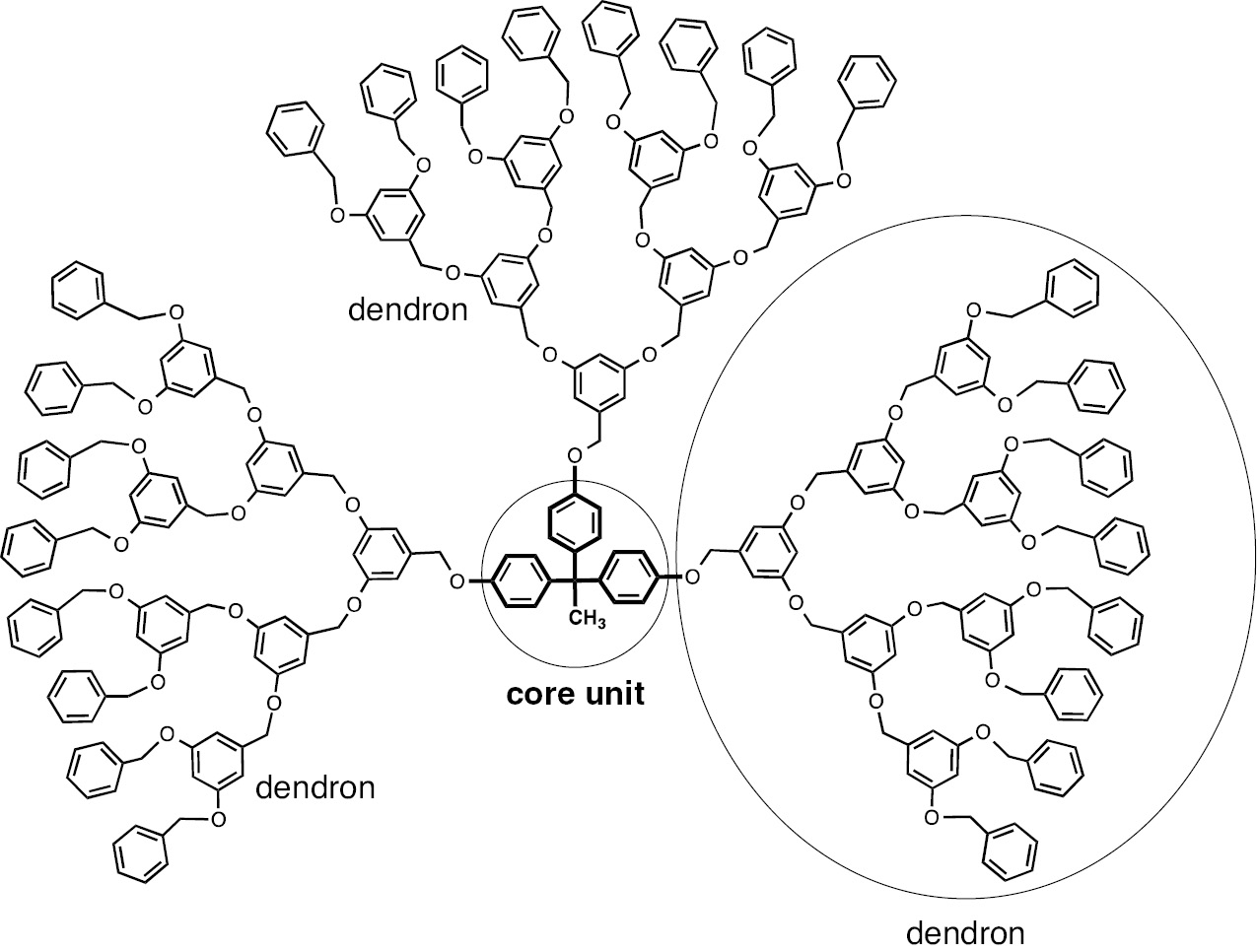

Representation of a regular dendrimer molecule highlighting the core unit and the dendrons.
See also: dendrimer molecule
Source:
PAC, 2019, 91, 523. 'Nomenclature and terminology for dendrimers with regular dendrons and for hyperbranched polymers (IUPAC Recommendations 2017)' on page 527 (https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2016-1217)
PAC, 2019, 91, 523. 'Nomenclature and terminology for dendrimers with regular dendrons and for hyperbranched polymers (IUPAC Recommendations 2017)' on page 527 (https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2016-1217)