https://doi.org/10.1351/goldbook.09130
Voltammetry in which a sinusoidal alternating potential of small amplitude (\(\pu{10 to 50 mV}\)) of constant frequency (\(\pu{10 Hz to 100 kHz}\)) is superimposed on a slowly and linearly varying potential ramp. The resulting alternating current is plotted versus imposed DC potential. The obtained AC voltammogram is peak-shaped.
Notes:
- The phase angle between the alternating current and imposed DC potential is measured in the case of AC voltammetry with phase detection.
- In cyclic AC voltammetry, a reverse potential scan is added to the usual forward potential scan.
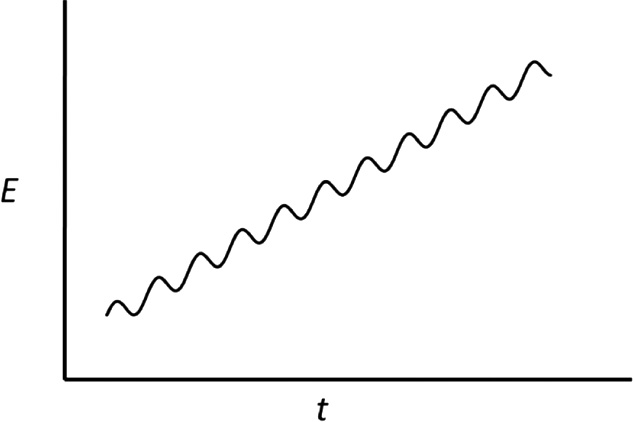
Waveform for AC voltammetry. The applied potential as a function of time is a sinusoidal alternating potential superimposed on a linearly increasing ramp.